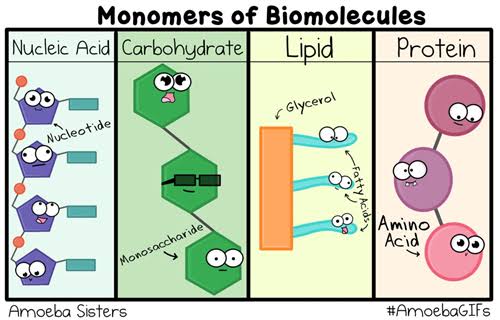
A GUIDE TO 2ND YEAR BIOCHEMISTRY - THE CHEMISTRY BETWEEN YOU AND BIOCHEMISTRY
Haven't been able to develop your chemistry with Biochemistry?
No worries, here we are, acting and reacting, until every single atom of yours has bonded with those of the Lippincott and Harper, that too covalently ;)
Ohkay so, you guessed it right, we'll be needing Lippincott the most, followed by Harper and for a very few topics Mark's.
But what comes to your rescue is, The collection of Slides By Dr. Noor Ul Ain and Dr. Nakshab, that are not only helpful but have pretty much everything that can be asked ( read *will be asked*)
Before beginning let's break two news - A good and a bad.
The bad news is, almost everything mentioned in your syllabus outline is important and must be done well - giving utmost importance to the clinical scenarios; and, the good news being, majority of the things are interlinked so if you get a good grip on your basics, it will turn out to be easier and fun!
So here we go!
LEGEND:
🔴 MOST IMPORTANT
🔵 IMPORTANT
⚪ LESS IMPORTANT
1. BIOENERGETICS:
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 6-
▪️ ENERGY:
⚪Endergonic & Exergonic reactions
⚪Free energy & free energy change
🔵ATP and other compounds as carriers of energy
▪️ ETC:
🔵Components and organization
🔵Reactions
🔵Redox potential Fig 6.12
🔵Methods of Electron transfer among the components of ETC and energy release during electron transport
▪️OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION:
🔴ATP synthesis in ETC & ATP Synthase
🔴Fig 6.13 - 6.15
🔴Inhibitors and Uncouplers of Oxidative phosphorylation
🔴Chemiosmotic hypothesis of Oxidative phosphorylation
🔴Membrane Transport Systems 6.17
HARPER
🔵Difference between high energy & low energy organophosphates
🔵Table 11.1
🔴All possible mechanism of ATP Production page 116-117
🔴Phosphagens and examples page 116-117
🔵Difference between Oxidases and Dehydrogenases Chap 12
🔴The Q Cycle page 128 fig-13-6
🔴Inhibitors of respiratory chain page 133 Fig 13-9
🔴The creatine phosphate shuttle
🔴& Clinical Aspects page 135
2. CARBOHYDRATES
▪️GLYCOLYSIS
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 8-
🔵Aerobic & Anaerobic Glycolysis
🔴Reactions and sites
🔵Energy yield of Glycolysis(both aerobic and anaerobic)
🔴Regulation of Glycolytic pathway
🔴Metabolic fates of Pyruvate
🔴Glucose Transporters Lehninger Table11.3
HARPER
🔴Table 17.1
▪️TCA CYCLE
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 9-
⚪Lactic acidosis
🔴PDH complex
Genetic deficiency of Pyruvate
🔴kinase and PDH
🔵Reactions of TCA cycle
🔴Regulation
HARPER:
🔴Energy yield- page 164
🔴Amphibolic role of the TCA cycle
▪️ GLUCONEOGENESIS
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 10-
🔵Precursors
🔵Reactions
🔴Regulation
🔴Biomedical significance
🔴Cori’s cycle & Glucose-Alanine
cycle
Harper
⚪Definition
🔵fig 19-5
▪️GLYCOGEN METABOLISM
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 11-
🔵Synthesis
🔵Importance of UDP glucose
🔵Reactions of Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
🔴Regulation of both pathways
🔵Importance of Glycogen phosphorylase a – a plasma glucose sensor
🔴Fig 11.12
🔴Glycogen storage diseases
Harper table 18-2
▪️ HMP PATHWAY
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 13-
🔵Reactions of Oxidative and Non-oxidative phases of HMP pathway
🔴NADPH Uses
🔴G-6PD Significance & deficiency
HARPER
🔵Page 197 diagram
🔴Uronic Acid Pathway page 200+205
▪️ MONOSACCHARIDE METABOLISM
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 12-
🔵Fructose metabolism & Disorders
🔴Fig 12.3
🔴Sorbitol metabolism & Hyperglycemia
🔵Metabolism of Galactose & Disorders
🔴Fig 12.5
HARPER
🔵Essential fructosuria and Hereditary fructose intolerance page 205
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 14
⚪GAGs Metabolism
🔵Mucopolysaccharidoses Fig 14.12
▪️BLOOD GLUCOSE REGULATION
🔵Chatterjea page 374-379
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 25-
🔴Diabetes Mellitus
3. LIPIDS
▪️ FATTY ACID METABOLISM:
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 16-
🔵De novo synthesis of Fatty acid
🔵Production of cytosolic acetyl CoA
🔴Fatty acid synthase multi enzyme complex (Slides or Harper)
🔵Reactions of cytosolic fatty acid synthesis
🔴Regulation of fatty acid synthesis
🔵Fig 16.11
▪️TRIACYLGLYCERIDES:
🔵Synthesis and storage of TAGs in body
⚪Mobilization of stored TAGs
🔵Regulation
🔵Fig16.13 - 16.15
HARPER:
⚪Fatty acid synthesis Pg 233
🔵Elongation of fatty acid chain page 237
🔵Synthesis of PUFA page 238-239
🔴Regulation page 236-237
🔴TAG regulation Page 262-263
▪️ FATTY ACID OXIDATION:
🔵Translocation of fatty acyl CoA into mitochondrial matrix
🔵Reactions of β -oxidation
🔴Carnitine Shuttle
🔴MCAD Deficiency
🔵Fig 16.16 - 16.20
🔵Fate of acetyl CoA
🔵Other types of fatty oxidation
🔵α–oxidation
🔵ω-oxidation
🔵Oxidation of odd-carbon fatty acids
HARPER:
🔴Fatty Acid activation page 224
🔴Table 22.1 – Energy yield of beta oxidation
🔵Fig22.3 & 22.4
▪️KETONE BODIES:
🔵Synthesis & utilization
🔵Fig 16.22- 16.24
HARPER
🔵Fig 22.7
🔵Page 227 – ketone utilisation by extra hepatic tissues
🔴Ketoacidosis
🔵Regulation of Ketogenesis page 229
▪️PHOSPHOLIPID SYNTHESIS:
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 17
🔵Metabolism
⚪Degradation of Phospholipids
🔵Deficiency of Lung Surfactant
🔵Metabolism of Glycolipids
⚪Biosynthesis of Ceramide, Sphingomyelin, and Gangliosides
⚪Degradation of Sphingolipids
🔵Sphingolipidoses Fig 17.19 17.20
HARPER
🔵Page 247- 248 – synthesis (phosphatidyl choline and phosphatidyl ethanolamine)
⚪Synthesis of Glycerol Ether Phospholipids (Cardiolipin and Platelet activating factor)
⚪Page 249 – degradation of pphospholipids
🔵Page 250-251 – sphingolipidoses
▪️ EICOSANOIDS:
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 17
🔴Synthesis
🔵Regulation
🔵Functions along with their Biomedical importance
🔵Fig 17.23
HARPER
🔴Page 239-243
▪️ CHOLESTEROL:
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 18-
🔵Reactions Fig 18.5
🔴Regulation Fig 18.6
🔴Fate and functions of Cholesterol in body
HARPER
🔵Page 267-269
▪️ CHOLESTEROL DEGRADATION – BILE ACIDS AND SALTS
🔴Biosynthesis of bile
🔵Fate of Bile acids
🔵Significance in health and disease
HARPER
🔵Page 273- 274
▪️ PLASMA PROTEINS:
🔵Synthesis
🔴Transport
🔴Fate of chylomicrons , VLDL , IDL ,LDL and HDL
🔴Athero genic effect of oxidized LDL
🔵Fig18.13
🔵Fig 18.15-18.18
🔵Fig. 18.20- 18.23
HARPER
🔵ApoproteinsPage 255
🔴Scavenger Receptors and atherosclerosis Page 258
Page - 274- 275
🔴Figures 25.3- 25.5
▪️ HYPERLIPIDEMIAS:
From Dr. Noor's Slides***
▪️ FATTY LIVER
HARPER
🔴Biochemical defects leading to Fatty liver page 259- 261
🔵Role of brown adipose Tissue page 264
▪️ DIETRY LIPID METABOLISM
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 15-
🔵Digestion, Absorption and Utilisation
🔵Cystic Fibrosis
🔵TAG and cholesteryl ester resynthesis
🔴Lipid malabsorption
🔴Fig 15.2 15.4 15.6 15.7
AND, REVIEW THE SLIDES CAREFULLY IN THE END
4. PROTEINS
▪️ NITROGEN METABOLISM:
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 19-
🔵Protein turnover
🔵Nitrogen balance- Positive and Negative
⚪Dietary protein digestion
🔴Degradation of Amino acids-
Removal of nitrogen from Amino Acids by Transamination and Deamination
🔵Sources of Ammonia in body
🔴Transport of ammonia fig 19.3
🔴Ammonia metabolism fig 19.9
🔴Ammonia toxicity fig 19.20
🔵Fate of Ammonia in body
🔴Urea cycle- Reactions and Regulation
🔴Metabolic disorders of the Urea cycle
🔴fig 19.14 - 19.16
HARPER:
🔴Inter-organ Amino Acid exchange in Normal Post-absorptive state -Chap 28 page 289
▪️ AMINO ACID METABOLISM:
LIPPINCOTT CHAP 20-
🔵Glucogenic and Ketogenic amino Acids
🔴Metabolism of individual amino acids like Glycine, Cysteine, Arginine, Proline , Phenylalanine ,Tyrosine ,
Histidine,Tryptophan ,Methionine
🔴Metabolic defects
HARPER:
🔴Amino acid carbon skeleton as a source of amphibolic intermediates fig 29.1
SATYA- chapter 15-
🔴Metabolism of the amino acids not given in Lippincott
🔴Metabolic defects in Amino acid metabolism like Phenylketonuria
Maple Syrup Urine disease (MSUD),
Histidinemia
Alkaptonuria
Cystathioninuria
Homocystinuria
Hyperprolinemia
Cystinuria
Cystinosis
Tyrosinemias
and Albinism
▪️ CATECHOLAMINES:
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 21-
Page 285 onwards
🔴Metabolism of Epinephrine and Norepinephrine , Creatine , Creatinine, Histamine, Gamma- Aminobutyrate, Serotonin, Melatonin, and Melaninq
HARPER:
🔵Glycine-Cleavage system of Liver Mitochondria page 302 fig 29-6
5. NUCLEOTIDES METABOLISM
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 22-
▪️ PURINES
🔵Reactions Fig 22.6 22.7
🔵Conversions of nucleoside monophosphates to diphosphates & triphosphates
🔵Synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides
🔵Fig 22.8 and 22.9
🔵Fig 22.10 22.12
🔴Ribonucleotide reductase formation and significance
🔵Fig 22.13
🔴Hydroxyurea
🔴Diseases associated with purine catabolism Fig 22.15
🔴Lesch Nyhan Syndrome
🔴Gout and its treatment Fig 22.18
🔴ADA deficiency
🔴Fig 22.5 – sources of individual atoms in purine rings
⚪Dietary degradation of Amino Acids Fig 22.14
▪️ PYRIMIDINES
🔵Synthesis n regulation
🔴Orotic aciduria Fig 22.21
🔴Diff b/w CPS1 n CPS 2 Fig 22.20
🔵Sources of individual atoms in pyrimidine rings Fig 22.19
🔵Fig 22.23
🔵Fig 22.24
HARPER
▪️ INTRODUCTION
CHAPTER 32
🔵Biomedical imp of nucleotides
🔵Syn and anti forms of nucleotides at n-glycosidic bond 341 fig 32.5
Nucleotide serving diverse physiological functions page 343
🔴Synthetic nucleotide analogs used in chemotherapy
CHAPTER 33
▪️ PURINES
🔵Fig 33.2
🔵Fig 33.3
🔵Reactions
🔴Multifunctional enzymes & their concerned reactions
🔵3 processes involved in purine synthesis
🔴Antifolate drugs page 348
🔵Synthesis of purines
🔵Salvage pathway
🔵Degradation of purines page 354 355 Fig 33.11
🔴Hyperuricemia in Von Gierke Disease (Slides)
▪️ PYRIMIDINES
🔵Fig 33.9
🔵Synthesis n regulation
🔵Catabolism of pyrimidines page 357
🔴Why catabolism of pyrimidines is less toxic than purines (page 355 harper last paragraph reason: pyrimidines form water soluble metabolite)
DO REVIEW THE SLIDES ASWELL
6. ENDOCRINOLOGY:
Here comes another good news, if you have done Endocrinology Physiology, you have almost done the Biochemistry too!
And if you haven't done it, you are all set to kill two birds with a single stone! :)
GUYTON:
▪️CHAPTER 75-
🔴General Characteristics of various types of Hormone Receptors
🔴MOA of various receptors
🔴Types and role of various kinds of Second Messengers
▪️CHAPTER 76 and 79-
Pituitary and Hypothalamic Hormones : ⚪Structure
🔵Biosynthesis
🔵Secretion
🔵Transport
🔴Regulation
🔵Catabolism
🔴Biologic Actions
of all Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones
🔴Disorders associated with the hypo and hyper states
▪️CHAPTER 77-
🔴Thyroid hormones- same as above
▪️CHAPTER 78-
🔴Adrenal hormones- same as above
▪️CHAPTER 80-
🔴Calcium regulating hormones and their disorders- same as above
▪️CHAPTER 81-
🔴Gonadal hormones- same as above
▪️LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 18
🔴Steroid Hormones(What is not in Guyton)
MARKS:
▪️CHAPTER 11-
🔵General Characteristics of various types of Hormone Receptors
🔴MOA of various receptors
🔴Types and Actions of Various kinds of G-proteins in mediating the actions of Hormones
🔴Signal Transduction Pathways of Various Hormones
▪️CHAPTER 43-
⚪Adrenal cortical hormones 782
⚪Adrenal medullary hormones page 791
⚪Pancreatic hormones page 785 and 786
Table 43.5
HARPER:
CHAPTER 41-
🔴An overview of Endocrine System Page 498
🔴Classification of Hormones based on their Mechanism of action and Chemical Nature
⚪Thyroid, pituitary, adrenal, Ca regulating hormones overview
AND OFCOURSE THE SLIDES ARE A MUST!
7. GENETICS:
As much as your Genes mean to you, Genetics means to Biochemistry!
So This needs to be dealt extra carefully;)
OFCOURSE YOU HAVE TO REVIEW ALL THE SLIDES, WITH OR AFTER THE BOOKS
▪️DNA AND REPLICATION
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 30:
⚪Basic structure overview
🔵Fig 30.26 30.27
⚪Karyotyping
🔴Replication of DNA - Steps of DNA Replication in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
🔴All the Enzymes used in the process alongwith RNA primer
🔵Fig 30.21
🔴DNA polymerase Functions Fig 30.23
🔴DNA Supercoiling and Topoisomerases
🔴Telomeres Fig 30.24
🔴Types of damage to DNA and DNA repair Fig 30.28 – 30.31
🔴Xeroderma Pigmentosum
HARPER
⚪Structure - Chap 34- page 359
🔴Chapter 35 - 35.3 35.4 35.6 35.9
▪️ TRANSCRIPTION
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 31
⚪Types Of RNA- overview
🔴Transcription – Steps of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic genes transcription
🔴RNA Polymerase Fig 31.6
🔴Inhibition of RNA polymerase by Rifampicin Fig 31.10
🔴Fig 31.12 - Fig 31.14
Post Transcriptional 🔴Modifications(processing) of RNA Fig 31.15 – 31.17
🔴Splicing Fig 31.18 31.19
LEHNINGER CHAPTER 26
Reverse Transcription in Retroviruses and its relation to Cancers and AIDS page 1086-1091
▪️ TRANSLATION:
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 32
🔵The Genetic code
🔴Altering the nucleotides sequence – Mutations Fig 32.3
🔵Huntington and other triplet expansion diseases Fig 32.4
🔴Frameshift Mutations Fig 32.5
🔴Components required for Protein synthesis
🔴Composition of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Ribosomes Fig 32.8
🔴Wobble Hypothesis Fig 32.9
🔵Steps of Protein Synthesis – initiation, Elongation, Termination
🔴Protein Factors Fig 32.14
🔴Protein synthesis Inhibition by antibiotics Fig 32.13
🔴Protein Targeting Fig 32.15
🔴Co and Post-Translational Modifications of Polypeptide Chains Fig 32.16
▪️ GENE EXPRESSION:
I HOPE YOU REMEMBER THE SLIDES?!
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 33-
🔵Figs 33.1 33.2 33.3
🔵Prokaryotic gene Regulation
🔴Lac Operon Fig 33.4 33.5
🔴Tryptophan Operon Fig 33.6
🔴Shine-Dalgarno Sequence
🔴Eukaryotic Regulation
🔴Galactose Circuit, Hormone Response System, Cell Surface Receptors
🔴Fig 33.9 - 33.11
🔵mRNA processing Fig 33.13
🔴Regulation of Transferin Receptors 33.14
🔴RNA interference
🔴Regulation through Variations in DNA : Example-
Immunoglobulin generation
▪️ BIOTECHNOLOGY:
LIPPINCOTT CHAPTER 34
🔵Restriction Endonucleases
🔴DNA Cloning and Vectors
Fig 34.5 – 34.8
🔴DNA sequencing Fig 34.9 34.10
🔵Probes Fig 34.11 34.12
🔴Southern Blotting 34.13
🔴RFLP and its significance Fig 34.15 - 34.19
🔴PCR - Use and Significance Fig 34.20 – 34.22
🔵Northern Blotting Fig 34.23
🔵Western Blotting Fig 34.24
🔵ELISA
🔵Fig 34.25
🔵Gene Therapy Fig 34.26
🔴Real time PCR from Chatterjee chap 18 page 289
▪️ ONCOGENESIS:
CHATTERJEE CHAPTER 46 +
MARKS CHAPTER 18
🔴Oncogenes and their Role in Carcinogenesis
🔴Mechanisms of Activation of Proto-Oncogenes
🔴Mechanism of Action of Oncogenes
🔴Tumour Supressor Gene
🔴Tumor Markers
🔴Oncogenic Viruses
🔴Genetic Basis of Disease -
Kaplan USMLE step 1 section II Medical Genetics Chap 1+3
THE SLIDES....OKAY OKAY YOU KNOW THAT!
8. pH
Ohkay so, another good news, Its the same what you did in 1st year. You'll only have to revise that, and ofcourse you know from where - Satya, Guyton and the electrolyte imbalances from Bishop.
9. INTEGRATION OF METABOLISM
🔵Lippincott Chapter 24-
The Feed Fast Cycle
&
⚪Lippincott Chapter 23-
Metabolic Effects of Insulin and Glucagon
And, So, here comes the best news of the day, THAT IS IT!
It is lengthy, requires your dedication, but is do-able and that too with all the fun by its side.
All the best, Happy Learning and feel free to ask if there's any confusion :)
Picture Credits: Giphy, The Ameoba Sisters, funfacts and Google images.